Medically Reviewed by: Edward C. Wade, M.D., F.A.C.S.
Today’s Top 4 Refractive Surgery Options
If you’re ready to enjoy clear, crisp vision without glasses or contact lenses, you have more choices than ever before. Modern refractive surgery options offer multiple ways to correct vision safely, effectively, and with long-lasting results.
Four of the top options today are LASIK, PRK, ICL, and RLE. To help you determine which might be right for you, keep reading to learn more about these refractive surgery options!
1. LASIK
LASIK, which stands for Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis, is one of the most popular and well-known vision correction procedures. It has helped millions of people worldwide correct their vision and eliminate their dependence on corrective eyewear.
What Happens During LASIK
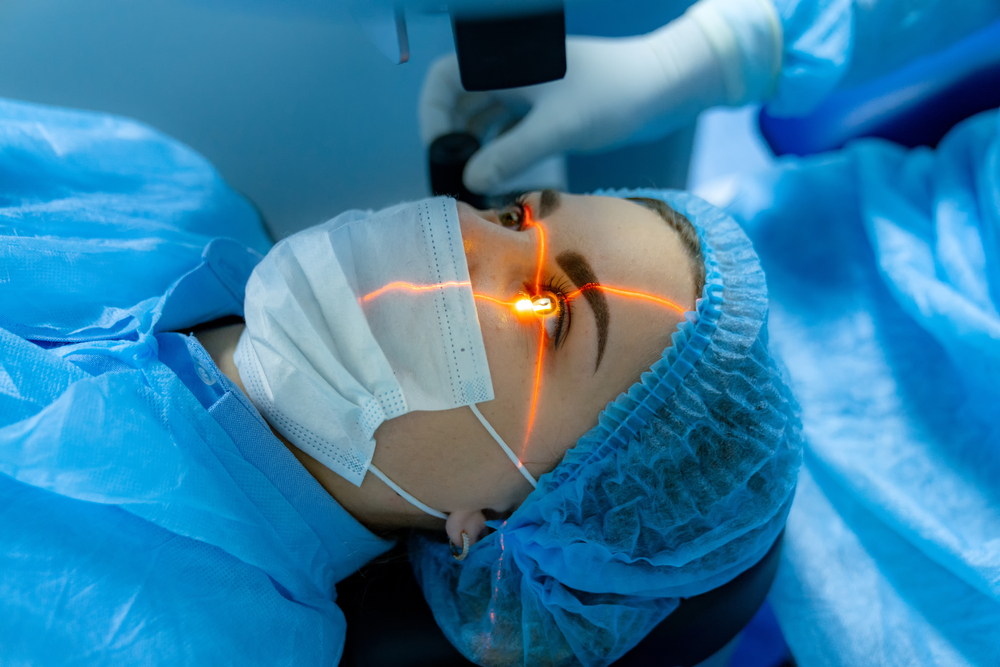
During LASIK, a thin flap is created on the surface of the cornea using a precise excimer laser. The laser reshapes the underlying corneal tissue to correct nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism.
After reshaping the cornea, the flap is gently repositioned and will heal naturally without stitches. The entire procedure usually takes about 15 minutes for both eyes, and the numbing drops applied before the surgery make it virtually painless.
Recovery from LASIK is typically fast, with many patients reporting noticeable improvement in their vision within a few hours. Most patients can return to normal activities, including work, within 1 to 2 days.
Who is a Good Candidate for LASIK?
Good candidates for LASIK must be at least 18 years old, have a stable prescription for at least one year, and healthy corneas with sufficient thickness. LASIK may not be suitable for patients with certain eye conditions, such as severe dry eye or thin corneas, unstable eye prescriptions, or an underlying health condition, such as diabetes or autoimmune disease, that could affect healing.
What are the Advantages of LASIK?
The biggest advantage of LASIK is its consistently high success rate. Many patients achieve 20/20 vision or better, with improved acuity, and the results are reliable and long-lasting.
2. PRK
PRK, or Photorefractive Keratectomy, was the first laser vision correction procedure to be approved by the FDA. The procedure is similar to LASIK, but involves removing the surface of the cornea, rather than creating a flap, to correct vision.
What Happens During PRK?
During PRK, the thin outer layer of the cornea, called the epithelium, is gently removed. An excimer laser is then used to reshape the underlying corneal tissue, restoring clear vision.
Once the cornea has been reshaped, a soft contact lens, known as an ocular bandage, is placed on the eye to protect it as the epithelium naturally regenerates. This healing process typically takes 3 to 5 days, and the ocular bandage is usually removed 1 week after surgery.
Recovery from PRK is usually slower than LASIK, and may cause temporary blurriness and mild discomfort as the epithelium heals. However, once the eyes fully recover, the results are often as precise and long-lasting as with LASIK.
Who is a Good Candidate for PRK?

PRK is ideal for patients over 18 with thinner corneas, irregular corneal surfaces, or those involved in contact sports who may be at higher risk of flap-related complications. It might also be a better option for patients with dry eye syndrome.
What are the Advantages of PRK?
The most significant benefits of PRK are that it does not create a flap and it disturbs less of the corneal tissue involved in tear production. This makes it a potentially safer option for patients with thin corneas, active lifestyles, or dry eyes.
3. ICL
ICL, which stands for Implantable Collamer Lens, is a popular option for people who are not good candidates for other laser-based procedures. It corrects vision using an implanted lens that sits inside the eye.
What Happens During ICL
During ICL surgery, a small incision is made at the base of the cornea, and a Collamer lens is implanted behind the iris and in front of the natural lens of the eye. The soft, biocompatible lens can correct nearsightedness and astigmatism by adjusting how light focuses on the retina, much like a removable contact lens.
The procedure usually takes about 20 to 30 minutes per eye, and vision often improves almost immediately afterward. Because no corneal tissue is removed, it is less invasive than other procedures, reducing the risk of complications.
For most patients, the recovery from ICL surgery is generally smooth and painless. While mild side effects can occur, these symptoms usually resolve quickly as the eye adjusts to the Collamer lens.
Who is a Good Candidate for ICL?
The best candidates for ICL surgery are adults aged 21 to 45 with moderate-to-severe nearsightedness or astigmatism and stable eye prescriptions. It’s also a strong choice for those with dry eyes or thin corneas who cannot safely undergo LASIK or PRK.
What are the Advantages of ICL?
A unique advantage of ICL is that it’s completely reversible. The Collamer lens can be removed or replaced if your prescription changes or if cataract surgery becomes necessary later in life.
4. RLE
RLE, or Refractive Lens Exchange, also sometimes called Clear Lens Exchange (CLE), is similar to cataract surgery, but is performed to correct refractive errors before cataracts develop. Instead of reshaping the cornea, RLE replaces the natural lens of the eye with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
What Happens During RLE?
During RLE, a tiny incision is made in the cornea, and ultrasound energy is used to remove the natural lens of the eye. An IOL is then implanted to correct nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia (age-related farsightedness).
RLE surgery is usually performed on each eye separately, with a short recovery period between procedures. The procedure usually takes about 15 to 20 minutes to complete, and most patients notice clearer vision within a few days.
Recovery after RLE is relatively quick, though it can take several weeks for vision to stabilize fully. IOLs are designed to last a lifetime, providing years of clear, crisp vision and preventing the formation of cataracts later in life.
Who is a Good Candidate for RLE?
RLE is best suited for patients who are at least 47 and experiencing presbyopia in addition to another refractive error. It can also be an option for patients with high degrees of refractive error that fall outside the acceptable range for other refractive surgery options.
What are the Advantages of RLE?

The main advantage of RLE is its permanence. It can provide a lifetime of clear vision, even for patients with presbyopia, and prevent cataracts, the most common cause of vision impairment among older adults.
Each refractive surgery option has unique advantages, but the right choice for you depends on your individual needs and vision goals. LASIK and PRK can provide years of clear vision by reshaping the cornea, while ICL and RLE work inside the eye for long-term vision correction.
Do you want to learn more about which refractive procedure might be right for you? Schedule a consultation at Eye Center of Texas in Houston, TX, today!
Related Articles
Financing Options Available
Apply today to find a financing option that meets your needs.
Our Locations
Houston/Bellaire
6565 W. Loop S., Suite 650Bellaire, TX 77401
Medical Office:
713-797-1010
Medical Fax:
713-357-7276
LASIK/Near Vision:
Office: 713-395-1515
Fax: 713-357-7278
Pasadena
4415 Crenshaw RoadPasadena, TX 77504
Medical Office:
281-977-8800
Medical Fax:
281-977-8877
Sugar Land
15200 S.W. Freeway, Suite 130Sugar Land, TX 77478
Medical Office:
281-277-1010
Medical Fax:
281-277-4504
Clear Lake
455 E. Medical Center Blvd., Suite 110Webster, TX 77598
Medical Office:
281-332-1397
Medical Fax:
281-282-9152
Katy
Greenhouse Medical Plaza2051 Greenhouse Road, Suite 110
Houston, TX 77084
Medical Office:
346-547-7070
Medical Fax:
281-214-2971
The Woodlands/Conroe
100 Medical Center Blvd., Suite 118Conroe, TX 77304
Medical Office:
936-647-1610
Medical Fax:
936-647-1620